Make a call
Blog Details

02
Sat
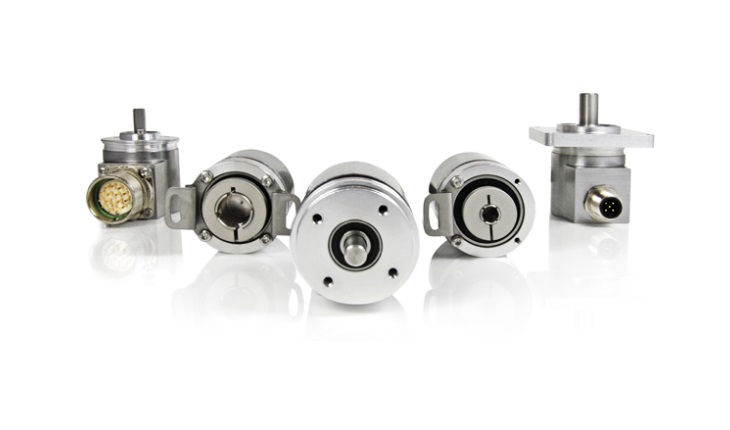
What is an Encoder, the Uses Classifications and famous brand popular models?
What is the encoder used for?
An encoder is a device that compiles and converts signals (such as bit streams) or data into a signal form that can be used for communication, transmission and storage. It converts angular displacement or linear displacement into electrical signals. The former is called a code disk and the latter is called a code ruler.
Encoders can be classified in many ways, as follows:
Classification by readout method
**Contact encoder:** It uses brush output to indicate whether the code state is "1" or "0" by contacting the conductive area or insulating area with the brush. It has a simple structure and low price, but the brush is easy to wear and has a limited life. It is often used in some low-precision control systems.
**Non-contact encoder:** The receiving sensitive element is a photosensitive element or a magnetic sensitive element. When a photosensitive element is used, the transparent area and the opaque area are used to indicate the state of the code. It is wear-free, has a long life and high sensitivity. It is often used in high-demand control systems such as aerospace and national defense.
Classification by the hole engraving method of the code disk
**Incremental encoder:** A pulse signal is issued for each unit angle, usually A phase, B phase, and Z phase output. A and B phases are pulse outputs that are delayed by 1/4 cycle from each other, which can distinguish between positive and reverse rotation, and the rising and falling edges of A and B phases can be taken for 2 or 4 times the frequency. Z phase is a single-turn pulse, which is used to measure the increment of displacement.
**Absolute encoder: **Corresponding to one circle, each reference angle sends a unique binary value corresponding to the angle. Multiple positions can be recorded and measured through an external circle recording device. The indicated value is only related to the starting and ending positions of the measurement, and has nothing to do with the intermediate process.
Classification by signal output type
**Voltage output encoder:** The output signal is a voltage signal with certain voltage amplitude and level characteristics, which can be directly connected to some devices or circuits that require voltage input.
**Open collector output encoder:** The output end adopts the form of open collector, and an external pull-up resistor is required to output the signal normally. It can easily realize the interface with multiple logic levels and has strong flexibility.
Push-pull complementary output encoder: It adopts a push-pull output circuit structure, which can provide strong driving ability, fast level conversion speed of output signal, and relatively strong anti-interference ability.
**Long-line drive output encoder:** It is suitable for long-distance signal transmission. It adopts differential signal transmission method, which can effectively suppress common mode interference and ensure the accuracy and stability of signal transmission.
Classification by mechanical installation form
**Shaft encoder:** It can be divided into clamping flange type, synchronous flange type and servo installation type, etc. It is connected to the rotating shaft of the equipment through the shaft to realize the measurement and feedback of rotational motion.
**Shaft sleeve encoder:** It can be divided into semi-empty type, full-empty type and large-diameter type, etc. It is usually sleeved on the shaft of the equipment and is suitable for some occasions with large shaft diameter or limited installation space.
Classification by working principle
**Photoelectric encoder:** It uses the principle of photoelectric conversion to convert rotation or linear displacement into electrical signal output. It consists of a light source, a grating disk and a photoelectric detector. It has the advantages of high precision, high resolution and high reliability.
**Magnetoelectric encoder:** It uses magnetic field changes to detect displacement. It consists of a magnetic ring, a magnetic head and a signal processing circuit. It has a simple structure, good durability and strong anti-interference ability. It is suitable for displacement measurement in harsh environments.
**Capacitive encoder:** It uses capacitance changes to detect displacement. It consists of a capacitor plate, a displacement body and a signal processing circuit. It has high precision, high resolution and high sensitivity, but is greatly affected by environmental factors such as temperature and humidity.
**Resistive encoder:** It measures position through a sliding resistor. The position of the sliding resistor determines the size of the output voltage, thereby reflecting the change of the mechanical position. It has a simple structure and low cost, but limited accuracy and life.
**Ultrasonic encoder:** It uses ultrasonic signals to measure position. It determines the position of an object by emitting ultrasonic waves and receiving reflected signals. It is mainly used in non-contact measurement occasions.
**Laser encoder:** It uses a laser beam and a reflector to detect position. The position of the mechanical component is determined by the reflected position of the laser beam on the reflector. It has very high accuracy, but high cost.
**Fiber optic encoder:** It uses fiber optic technology to transmit position information. It can work in extreme environments, such as high temperature, high pressure and severe electromagnetic interference.
The following are some of the best-selling encoders from international brands:
**HEIDENHAIN**
ERN 1387 Series: It is an incremental rotary encoder with high precision and high resolution. It is often used in machine tools, automated production lines and other fields that require extremely high position and speed control accuracy.
RCN 223 Series: Absolute encoder with high single-turn resolution, which can provide accurate position feedback. It is suitable for equipment that requires long-term stable operation and strict position accuracy requirements, such as large gantry milling machines, machining centers, etc.
**Tamagawa**
TS5208N173 Series: Incremental photoelectric encoder, known for its high precision and high reliability, is widely used in robot joint control, semiconductor manufacturing equipment and other fields.
TAS464D Series: Absolute encoder with multiple output interfaces to meet the needs of different control systems. It is often used in CNC machine tools, automatic assembly lines, etc.
**SICK**
DGS80 Series: Large aperture encoder, easy to install, can adapt to different shaft diameters, often used in logistics transportation equipment, large rotating machinery, etc.
DLS40 series: incremental encoder, with good anti-interference ability and stability, suitable for general position and speed measurement in the field of industrial automation.
**Baumer**
HMG absolute encoder: adopts multi-turn technology, with high resolution and reliability, suitable for large mechanical equipment such as cranes and port equipment that require precise position measurement.
OMM60 incremental encoder: with compact design and multiple electrical interfaces, it can be widely used in packaging machinery, printing machinery and other fields.
**Nemicon**
OVW2 series: such as OVW2-10-2MHC, OVW2-12-2MHT, etc., incremental photoelectric rotary encoder, high cost performance, widely used in elevators, textile machinery and other fields.
OSS series: such as OSS-036-2HC-24-050-00E, is an incremental encoder with high accuracy, often used in some automation equipment with certain requirements for position accuracy.
**Pepperl+Fuchs**
RHI90N series: such as RHI90N-0HAAAR61N-01, RHI90N-0HAK1R61N-01024, etc., absolute encoders, with high protection level, can work stably in harsh environments, and are commonly used in metallurgy, mining and other industries.
RVI58N series: both incremental and absolute, such as RVI58N-011K1R61N-01024, with multiple resolutions to choose from, suitable for a variety of industrial automation scenarios.
**Hengstler**
AC58 series: absolute encoders, such as AC58/1212EK.42DPZ, AC58/0812ES.41PGB-F0, etc., support a variety of fieldbus protocols, and are widely used in industrial automation control systems.
RI64 series: Incremental encoders, such as RI64/4096-BW7H9IB-A5-O, offer high accuracy and reliability for applications such as motor feedback and mechanical motion control.
Tags:

Our mission
Build strong relationships
with clients
Take responsibility for our customers, create value continuously,
and become a
trustworthy partner for industrial intelligence and connectivity.



